How to Spot a Shoplifter: Tips and Techniques for Quick Detection
In This article
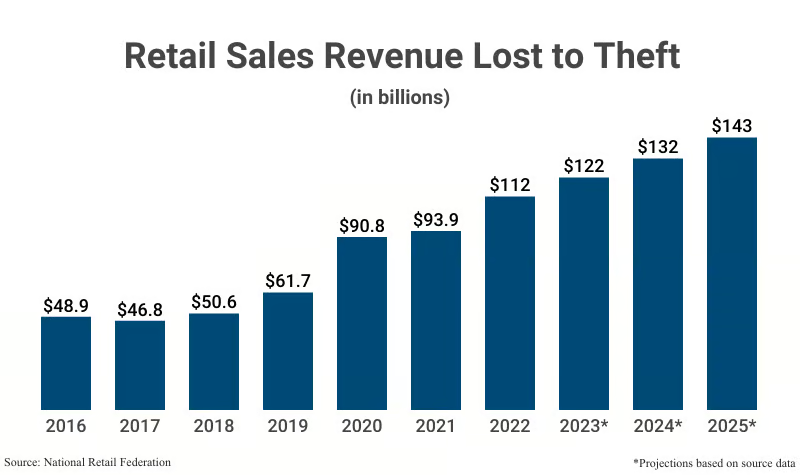
To stop a shoplifter, you must know how to spot a shoplifter—reported shoplifting incidents increased 24% during the first half of 2024. Retailers’ annual losses are approximately $13 billion, or more than $35 million per day. Retail stores and other commercial establishments require a multi-layered prevention strategy to spot shoplifters. These include employee training, investing in advanced security measures such as AI-powered cameras, and reassessing merchandise placement throughout the store.
This strategic approach can enhance early detection, which is crucial for preventing shoplifting, inventory loss, and revenue decline, while also protecting employees and shoppers, maximizing foot traffic, and deterring repeat offenders. Identifying a shoplifter can be tricky. Various studies reveal that one in eleven Americans has shoplifted, representing all demographic groups. More are adults than juveniles, more are men than women, and approximately 30% are repeat offenders. One in five lives in households with annual incomes exceeding $75,000. Stereotyping shoplifters, therefore, can be a deterrent to spotting a shoplifter.
Several other factors must be considered when learning how to spot a shoplifter. Some types of merchandise are most susceptible to shoplifting. Electronics account for 30% of shoplifting, and luxury cosmetics are second at 18%. Approximately two-thirds of all shoplifting incidents occur in urban areas, primarily due to population concentration and the higher number of retail establishments. Theft incidents at suburban malls have increased substantially since 2022. Unsurprisingly, states with higher unemployment rates tend to experience more shoplifting incidents; however, economic hardship often compels people to engage in shoplifting, regardless of the state or region.
Common Signs of a Shoplifter
Since most shoplifters are first-time offenders, it may be easier to spot them than repeat offenders due to the lack of experience of those first-timers. Nonetheless, there are common signs that almost all shoplifters share, along with their best shoplifting tips.
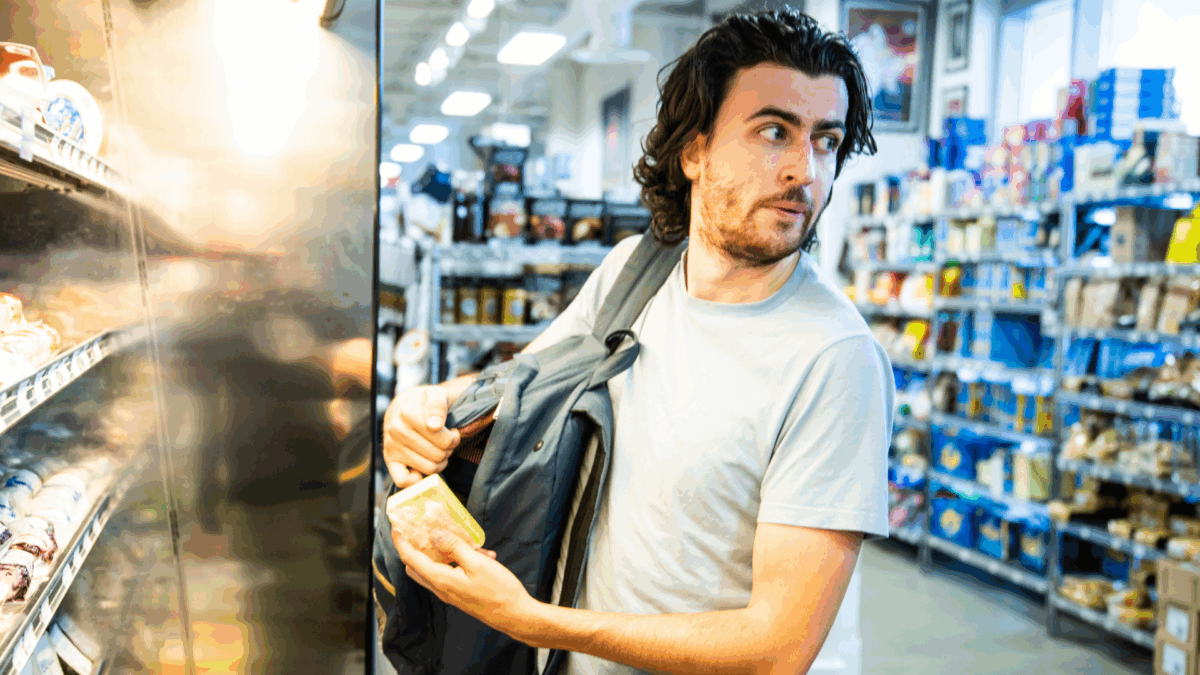
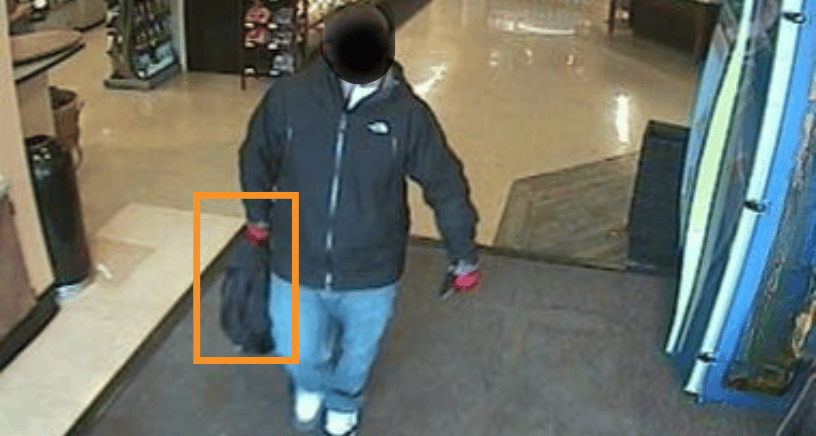
- More than half of shoplifters use clothing or bags to conceal stolen merchandise. Spotting customers wearing bulky clothing, especially during warmer months, or carrying numerous shopping bags that appear half-empty can be identifying signs.
- Although not exclusive to inexperienced shoplifters, they are more likely to follow the movements of store employees instead of focusing on merchandise.
- Similarly, potential shoplifters may glance toward visible camera placements and other places they think cameras may be mounted.
- The movement of a shoplifter throughout the store may seem peculiar compared to that of other shoppers, especially if they spend little time examining merchandise and move from one display or rack to another quickly.
- Potential shoplifters can appear nervous or apprehensive, or constantly check their phones, purses, and wallets.
Behavioral Patterns of Shoplifters
There are only so many shoplifting tactics, so if you want to know how to spot a shoplifter, then look for patterns in their behavior. These patterns may help identify repeat offenders because they employ previously successful tactics. Keep in mind: More than 70% of all shoplifting incidents are unplanned, impulsive behavior.
- Shoplifters often wait until a retail store is crowded during peak shopping periods, either while the staff is busy with other shoppers or when they visit the backroom to fulfill their requests and restock merchandise.
- Multiple requests of the staff to bring merchandise from the backroom is another tactic for distracting the staff.
- Some shoplifters will visit a store multiple times to learn when the fewest employees are working, such as during meal breaks, or to identify targeted merchandise.
- Loitering at the store entrance and then leaving quickly is another pattern of shoplifters.
- Shoppers who seem uninterested in talking with employees when they offer assistance and exhibit signs of nervousness.
- Shoplifters sometimes work in teams but don’t shop together, quickly circulating throughout the store. They may be planning to shoplift multiple merchandise, or some may cause a distraction so another can shoplift without being seen.
Techniques for Quick Detection of Shoplifters
Store employees are the front line in quickly detecting shoplifters and reducing loss prevention. Thorough training in the signs and behavioral patterns of shoplifters is crucial. This training empowers employees to manage active shoplifting incidents effectively, maintaining a friendly and helpful demeanor while facilitating a quick and non-violent resolution.
Providing employees with a daily store tour before opening can be helpful. Know where new and high-priced merchandise is displayed, review the placement of security cameras and deterrent systems, and maintain clear sight lines throughout the store, including entrances and exits.
RFID tagging of merchandise remains a common practice in many stores and has proven to be effective. Merchandise with RFID tags hidden in clothing or bags can be located in real-time, providing reassurance that shoplifters can be detected and causing less disruption to the shopping environment.
How to Approach Suspected Shoplifters
When a suspected shoplifter is spotted, the store manager and employees must remain calm and observe the suspicious activity to ensure that a shoplifting incident has occurred. This calm and observant approach helps maintain control of the situation and ensures a shoplifting incident has happened before taking any action.
A hurried or confrontational approach can be counter-productive when surveillance indicates it’s time to approach a suspected shoplifter. Aggressive tactics can escalate the situation, disrupt, and even cause other shoppers to leave the store. Offering shopping assistance or explaining the quality and value of the merchandise near the suspected shoplifter is a better approach. Talking with the suspected shoplifter allows a store manager or employee to better assess any bulky clothing, half-empty shopping bags, and behavioral patterns.
Using these techniques to approach a suspected shoplifter is more likely to keep them calm, deter disruptive behavior or even violence, and quickly and quietly escort them to the backroom or an office. Role-playing can help employees practice these procedures and correct any errors before they are involved in an actual shoplifting incident.
Legal Considerations in Handling Shoplifters
The legal implications of a shoplifting incident emphasize the need for comprehensive employee training. Stores should have comprehensive policies related to the legalities of shoplifting incidents, including the legal procedures for detaining and reporting a shoplifter, the rights of the shoplifter, and the store’s responsibilities. Managers and employees should be thoroughly trained in those policies and local statutes.
Inviting a local law enforcement officer and/or an attorney to review the legal considerations in handling shoplifters with employees is a wise decision. They can also explain at what stage in a shoplifting incident law enforcement should be contacted, and how to engage with law enforcement during and after the incident. Training from a police officer or attorney can also include the legal procedures for securing evidence and presenting it to law enforcement.
Shoplifters who have been caught red-handed still have rights, including data privacy, which must be respected. Law enforcement makes any arrest, and the judicial system determines guilt or innocence. Employees must also feel protected and be aware of their rights when engaging with and detaining a shoplifter.
Preventative Measures to Reduce Shoplifting
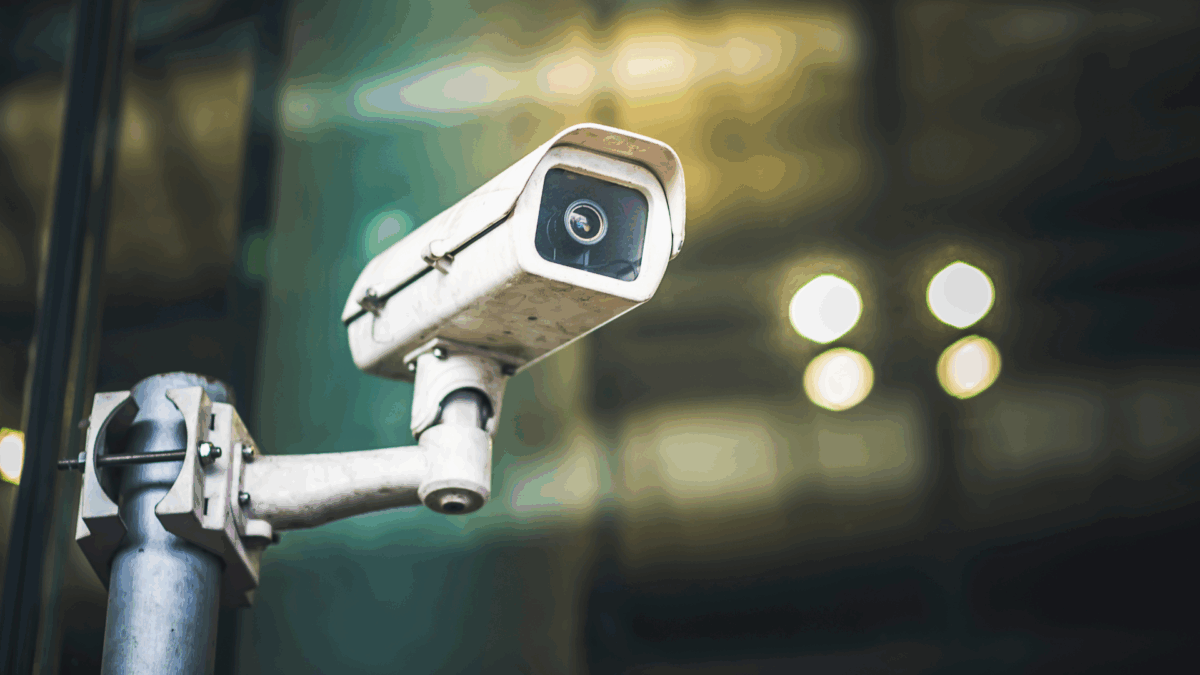
Employee awareness and advanced security technologies are more likely to prevent shoplifting. Video surveillance has been and continues to be a primary tool for quickly detecting shoplifters. Although some may think cameras should be positioned in high corners or on the ceiling, the most effective locations are at eye level or a little higher. Not only will this provide a comprehensive view of all areas of a store—entrances and exits, high-value merchandise, and checkout counters—but it will also make it clear to shoppers that they are being monitored.
Adding prominently positioned signage indicating that video cameras are in use can deter shoplifters and provide all shoppers with peace of mind. Ownership and management should also review a store’s lighting pattern to ensure that the most vulnerable areas are well-lit.
Some stores have found it necessary to lock specific merchandise in glass cases to deter shoplifting. Doing so requires careful consideration to strike a balance between prevention and providing customers with the shopping experience they expect. This can be particularly challenging for small, local stores with a loyal customer base wanting to touch and inspect merchandise.
Although AI capabilities are now being integrated into video surveillance cameras, upgrading to high-definition cameras and advanced theft-detection tools equipped with these capabilities is a worthwhile investment. Better image quality enables law enforcement to more easily identify suspicious individuals and their shoplifting activities, facilitating the apprehension of suspects. Many AI-powered tools and systems enable management to remotely monitor and access a store via a mobile device.
Ownership and management should regularly review store layouts to ensure that employees and personnel have a clear view of all aisles and displays, particularly those featuring the highest-value or luxury merchandise, which is more likely to be targeted by shoplifters.
Conclusion
As with any crime, minimizing the effects of shoplifting is the most practical goal. In an open society with numerous stores competing to attract high foot traffic and promote special offers and pricing to maximize sales and revenue, shoplifting will always be a threat.
Dampening that threat begins with knowing how to spot a shoplifter. The most critical skill is recognizing the common signs and behavioral patterns of shoplifters. A carefully planned store layout, merchandise displays, and good lighting will make it easier to spot shoplifting activities.
Early detection is also enhanced with the right mix of surveillance technologies, which even small business owners can invest in to deter shoplifting and minimize business losses.
Discover more about DTiQ’s loss prevention solutions here.
Frequently Asked Questions About Spotting Shoplifters
Q: What should I do if I suspect someone is shoplifting?
A: Remain calm and don’t exhibit any body language or other movements that may reveal to a suspected shoplifter that they are being watched. Initially, observe the person to have a clearer view. Moving to a location nearer the alleged shoplifter and inspecting or rearranging merchandise will appear like regular store activity and may validate suspicions. Use the techniques in the section above, How to Approach Suspected Shoplifters, to engage with a suspected shoplifter and determine if further actions are required.
Q: Can store employees legally detain a shoplifter?
A: The answer to this question depends on the store’s legal procedures and local statutes. Consulting with local law enforcement and/or an attorney is highly recommended, so that ownership, management, and employees understand the legal rights of suspected shoplifters and detain them in a legally and professionally responsible manner.
Q: What are the best security technologies to prevent theft?
A: High-quality, AI-powered video cameras are the most utilized security technologies. In 2021, approximately 84.5 million security cameras were in operation in the United States. Cameras are the eyes of a store’s anti-theft system, while advanced monitoring equipment serves as its brain. Observing and identifying shoplifters requires coordinated use of both to maximize loss prevention.
Q: How can small businesses afford shoplifting prevention measures?
A: Before investing in new or advanced surveillance technologies, small business owners should carefully assess their specific loss prevention issues. More training may be needed. Asking law enforcement and/or an attorney to address employees is typically less costly than hiring a training consultant or company. Coordinating loss-prevention efforts with nearby stores, especially in a mall setting, can provide small business owners with insights and practical knowledge. Locked cases are a low-cost preventive step. Instead of an RFID tagging system, light-sensitive tags will trigger an alarm when placed in a pocket or bag. Hooks that only allow the removal of one product are another low-cost tool.